1. Moon
is a -
(a) Luminous
object
(b) Non-luminous
object
(c) Sometimes
luminous and sometimes non-luminous
(d) Cannot
say
ANS –
Non-luminous object
2. Air
is a -
(a) Transparent
medium for light
(b) Translucent
medium for light
(c) Opaque
medium for light
(d) None
ANS –
transparent medium for light
3. When
light falls on a highly polished surface, most of it-
(a) is
reflected
(b) is
refracted
(c) is
absorbed
(d) all
the above three in equal proportion
ANS –
is reflected
4. The
straight line path along which light travels is called _____ of light.
(a) ray
(b) beam
(c) bundle
(d) None
ANS –
ray
5. Which
of the following letter will show lateral inversion in a plane mirror?
(a) M
(b) N
(c) O
(d) A
ANS –
N
6. A
virtual image formed by a mirror-
(a) is
always formed behind the mirror
(b) may
form behind the mirror
(c) is
always formed in front of the mirror
(d) may
form in front of the mirror
ANS –
is always formed behind the mirror
7. If
the angle of incidence is 500, then calculate the angle between the incident
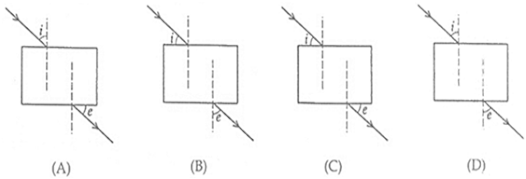
ray and the reflected ray:
(a) 500
(b) 1000
(c) 1300
(d) 800
ANS -
1000
8. An
object A is placed at a distance ‘d’ in front of a plane mirror. If one stands
directly behind the object at distance S from the mirror, then the distance of
the image of A from the individual is:
(a)
2S
(b) 2d
(c) S+d
(d) S+2d
ANS –
s+d
9. A
plane mirror is placed vertically facing due north. An arrow pointing
north-east is kept just in front of this mirror. In which of these direction
will the arrow point in the image:
(a) North-east
(b) South-east
(c) South-west
(d) North-west
ANS –
South-east
10.
If we want to see our full image then the minimum size of the plane mirror:
(a) Should
be twice of our height
(b)
Should be of our height
(c)
Should be half of our height
(d) Depends
upon our distance from mirror
ANS –
should be half of our height
11. Two
mirrors are inclined at an angle 600, an object is placed between them. Then number
of images formed will be:
(a) 6
(b) 5
(c) 7
(d) 9
ANS -
5
12. To
get 9 multiple images the angle between the plane mirrors should be:
(a) 600
(b) 360
(c) 500
(d) 900
ANS –
360
13. Two
plane mirrors are at right angles to each other. A man stands between them and
combs his hair with the right hand. How many images will be seen using his left
hand?
(a) None
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 2
ANS -
3
14. If
an object is placed symmetrically between two plane mirrors, inclined at an
angle 720, then the total number of images formed will be:
(a) 5
(b) 4
(c) infinite
(d) 7
ANS -
4
15.
Plane mirrors are arranged parallel to each other to get:
(a) A
single image
(b) Two
images
(c) A
large number of reflected images
(d) No
image
ANS –
A large number of reflected images
16. The
central point of the mirror is called-
(a) focus
(b) pole
(c) centre
of curvature
(d) focal
length
ANS –
pole
17. The
Focal length of a mirror depends on-
(a) The
material of the mirror
(b) Thickness
of silver coating
(c) Aperture
of the mirror
(d) Radius
of curvature
ANS –
radius of curvature
18. The
radius of curvature of a plane mirror is-
(a) infinity
(b) zero
(c) 10
cm
(d) None
ANS –
infinity
19. Focal
length of a concave mirror is-
(a) negative
(b) positive
(c) depends
on the placement of object
(d) depends
on the location of image
ANS –
negative
20.
Identify the device used as a spherical mirror in following cases, when the
image formed is virtual and erect in each case
(a) Object
is placed between device and its focus, image formed is enlarged and behind it.
(b) Object
is placed between infinity and device, image formed is diminished and between
pole and focus, behind it.
ANS –
(a) Concave mirror, (b) convex mirror
21.
Magnification of a mirror comes out to be always positive. The mirror is-
(a) concave
(b) convex
(c) may
be concave or convex
(d) None
ANS –
Convex
22. The
unit of magnification is-
(a) m
(b) km
(c) cm
(d) None
ANS –
None
23. Magnification
produced by a mirror is +1.5. The mirror is-
(a) concave
(b) convex
(c) may
be concave or convex
(d) None
ANS –
concave
24.
A convex mirror is used as rear view mirror because,
(a) It
forms erect image
(b) It
forms diminished image
(c) It
increases the field of view (driver is able to view a much larger distance)
(d) Image
is formed between pole and focus
(e) For
all of the above reasons
ANS –
For all of the above reasons
25.
Magnification produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles:
(a) is
less than one
(b) is
more than one
(c) is
equal to one
(d) Can
be more than or less than one depending upon the position of the object in
front of it
ANS –
is less than one
26.
A point object is placed at a distance of 20 cm from a convex mirror of focal
length 20 cm. The image will form at-
(a)
infinity
(b)
at focus
(c)
behind the mirror
(d) pole
ANS –
behind the mirror
27.
Rays from sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where
should an object be so that the size of its image is equal to the size of the
object?
(a) 15
cm in front of the mirror
(b) 30
cm in front of the mirror
(c) Between
15 cm and 30 cm in front of the mirror
(d) More
than 30 cm in front of the mirror
ANS –
30 cm in front of the mirror
28.
In torches, search lights and headlights of vehicles the bulb is placed:
(a) Between
the pole and the focus of the reflector
(b) Very
near to the focus of the reflector
(c) Between
the focus and centre of curvature of the reflector
(d) At
the centre of curvature of the reflector
ANS –
very near to the focus of the reflector
29.
What will be the nature of the image formed of an object which is placed
between infinity and pole of convex mirror?
(a) Behind
the mirror, between P and F and virtual and erect
(b) Behind
the mirror, between P and F, virtual and inverted
(c) In
front of mirror, real and erect
(d) In
front of mirror, virtual and erect
ANS –
Behind the mirror, between P and F and virtual and erect
30.
If you hold a convex mirror in front of a building, you will see the image as
(a) An
enlarged and erect image of the building
(b) A
diminished and erect image of the building
(c) An
enlarged and inverted image of the building
(d) Diminished
and inverted image of the building
ANS –
a diminished and erect image of the building
31. The
image formed by a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm is one-fourth the size of
the object. What is the distance of the object from the mirror?
(a) 30
cm
(b) 90
cm
(c) 120
cm
(d) 240
cm
ANS –
90 cm
32. Radius
of curvature of a concave mirror is 40 cm and the size of image is twice as that
of the object. Then, u is-
(a) 20
cm
(b) 30
cm
(c) 40
cm
(d) 10
cm
ANS –
10 cm
33. A
virtual image three times the size of the object is obtained with a concave
mirror of radius of curvature 36 cm. The distance of the object from the mirror
is-
(a) 20
cm
(b) 10
cm
(c) 12
cm
(d) 5
cm
ANS –
12 cm
34. An
object is placed at a distance of 0.25m in front of a plane mirror. The
distance between the object and image will be
(a)
0.25 m
(b)
1.0 m
(c)
0.5 m
(d)
0.125 m
ANS –
0.5 m
35. The
angle of incidence for a ray of light having zero reflection angle is
(a) 0
(b)
30°
(c)
45°
(d)
90°
ANS –
0
36. For
a real object, which of the following can produce a real image?
(a)
Plane mirror
(b)
Concave mirror
(c)
Concave lens
(d)
Convex mirror
ANS –
concave mirror
37. Which
of the following mirror is used by a dentist to examine a small cavity?
(a)
Convex mirror
(b)
Plane mirror
(c)
Concave mirror
(d)
Combination of convex and concave mirror
ANS –
concave mirror
38. An
object at a distance of 30 cm from a concave mirror gets its image at the same
point. The focal length of the mirror is,
(a) –
30 cm
(b)
30 cm
(c) –
15 cm
(d)
+15 cm
ANS :
-15 cm
39. An
object at a distance of + 15 cm is slowly moved towards the pole of a convex
mirror. The image will get
(a)
shortened and real
(b)
enlarged and real
(c)
enlarge and virtual
(d)
diminished and virtual
ANS :
diminished and virtual
40. A
concave mirror of radius 30 cm is placed in water. Its focal length in air and
water differ by
(a)
15
(b)
20
(c)
30
(d) 0
ANS :
0
41. A
concave mirror of focal length 20 cm forms an image having twice the size of
object. For the virtual position of object, the position of object will be at
(a)
25 cm
(b)
40 cm
(c)
10 cm
(d)
At infinity
ANS :
10 cm
42. The
image formed by concave mirror is real, inverted and of the same size as that
of the object. The position of object should be
(a)
at the focus
(b)
at the centre of curvature
(c)
between focus and centre of curvature
(d)
beyond centre of curvature
ANS :
at the centre of curvature
43. The
nature of the image formed by concave mirror when the object is placed between
the focus (F) and centre of curvature (C) of the mirror observed by us is
(a)
real, inverted and diminished
(b)
virtual, erect and smaller in size
(c)
real, inverted and enlarged
(d)
virtual, upright and enlarged
ANS –
real, inverted and enlarged
44. The
nature of image formed by a convex mirror when the object distance from the
mirror is less than the distance between pole and focal point (F) of the mirror
would be
(a)
real, inverted and diminished in size
(b)
real, inverted and enlarged in size
(c)
virtual, upright and diminished in size
(d)
virtual, upright and enlarged in size
ANS –
virtual, upright and diminished in size
45. If
a man’s face is 25 cm in front of concave shaving mirror producing erect image
1.5 times the size of face, focal length of the mirror would be
(a)
75 cm
(b)
25 cm
(c)
15 cm
(d)
60 cm
ANS –
75 cm
46. As
light travels from a rarer to a denser medium it will have
(a)
increased velocity
(b)
decreased velocity
(c)
decreased wavelength
(d)
both (b) and (c)
ANS –
both (b) and (c)
47. The
angle of incidence i and refraction r are equal in a transparent slab when the
value of i is
(a)
0°
(b)
45°
(c)
90°
(d)
depend on the material of the slab
ANS –
00
48. The
refractive index of transparent medium is greater than one because
(a)
Speed of light in vacuum < speed of light in tansparent medium
(b)
Speed of light in vacuum > speed of light in tansparent medium
(c)
Speed flight in vacuum = speed of light in tansparent medium
(d)
Frequency of light wave changes when it moves from rarer to denser medium
ANS –
Speed of light in vacuum > speed of light in tansparent medium
49. You
are given three media A, B and C of refractive index 1.33, 1.65 and 1.46. The
medium in which the light will travel fastest is
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d)
equal in all three media
ANS –
A
50. Light
from the Sun falling on a convex lens will converge at a point called
(a)
centre of curvature
(b)
focus
(c)
radius of curvature
(d)
optical centre
ANS –
Focus
51. Large
number of thin stripes of black paint are made on the surface of a convex lens
of focal length 20 cm to catch the image of a white horse. The image will be
(a) a
zebra of black stripes
(b) a
horse of black stripes
(c) a
horse of less brightness
(d) a
zebra of less brightness
ANS –
a horse of less brightness
52. A
divergent lens will produce
(a)
always real image
(b)
always virtual image
(c)
both real and virtual image
(d)
none of these
ANS –
always virtual image
53. When
object moves closer to convex lens (from infinity to F), the image formed by it
shift
(a)
away from the lens
(b)
towards the lens
(c)
first towards and then away from the lens
(d)
first away and then towards the lens
ANS –
away from the lens
54. When
object moves closer to a concave lens the image by it shift
(a)
away from the lens on the same side of object
(b)
toward the lens
(c)
away from the lens on the other side of lens
(d)
first towards and then away from the lens
ANS –
towards the lens
55. A
magnified real image is formed by a convex lens when the object is at
(a) F
(b)
between F and 2F
(c)
2F
(d)
(a) and (b) both
ANS –
(a) and (b) both
56. The distance between the optical centre and point of convergence is called focal length in which of the following cases?
ANS –
(c)
57. A
10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror. A 5 mm
long image of the awl pin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror. The focal
length of this mirror is
[NCERT Exemplar Problems]
(a) –
30 cm
(b) –
20 cm
(c) –
40 cm
(d) –
60 cm
ANS
– -20 cm
58. Figure
shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index
of the medium B relative to medium A is, [NCERT Exemplar Problems]
ANS –
(a)
59. A
light ray enters from medium A to medium B as shown in figure. The refractive
index of medium B relative to A will be,
[NCERT Exemplar Problems]
(a)
greater than unity
(b)
less than unity
(c)
equal to unity
(d)
zero
ANS –
greater than unity
60. Beams
of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through
the holes C and D respectively as shown in the figure. Which of the following
could be inside the box?
[NCERT Exemplar Problems]
(a) A
rectangular glass slab
(b) A
convex lens
(c) A
concave lens
(d) A
prism
ANS –
A rectangular glass slab
61. A
beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of the
hole on the other face of the box as shown in the figure. Which of the
following could be inside the box?
[NCERT Exemplar
Problems]
(a)
Concave lens
(b)
Rectangular glass slab
(c)
Prism
(d)
Convex lens
ANS –
Convex lens
62. Which
of the following statements is/are true? [NCERT Exemplar Problems]
(a) A
convex lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
(b) A
convex lens has -4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
(c) A
concave lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
(d) A
concave lens has – 4 dioptre having a focal 0.25 m
ANS –
both (a) and (d)
63. A
full length image of a distant tall building can definitely be seen by using,
[NCERT Exemplar
Problems]
(a) a
concave mirror
(b) a
convex mirror
(c) a
plane mirror
(d)
both concave as well as plane mirror
ANS –
a convex mirror
64. The
laws of reflection hold good for [NCERT Exemplar Problems]
(a)
plane mirror only
(b)
concave mirror only
(c)
convex mirror only
(d)
all mirrors irrespective of their shape
ANS –
all mirrors irrespective of their shape
65. The
path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab
traced by four students are shown as A, B, C and D in figure. Which one of them
is correct?
[NCERT Exemplar Problems]
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS –
B
66. In
which of the following, the image of an object placed at infinity will be
highly diminished and point sized?
[NCERT
Exemplar Problems]
(a)
Concave mirror only
(b)
Convex mirror only
(c)
Convex lens only
(d) Concave
mirror, convex mirror, concave lens and convex lens.
ANS –
Concave mirror, convex mirror, concave lens and convex lens
67. Image
formed by reflection from a plane mirror is
(a)
real and inverted
(b)
virtual and erect
(c)
real and erect
(d)
virtual and inverted
ANS –
virtual and erect
68. If
an incident ray passes through the focus, the reflected ray will
(a)
pass through the pole
(b)
be parallel to the principal axis
(c)
retrace its path
(d)
pass through the centre of curvature
ANS –
be parallel to the principal axis
69. Magnifying
power of a concave lens is
(a)
always > 1
(b)
always < 1
(c)
always = 1
(d)
can have any value
ANS –
always < 1
70. The
image formed by a convex lens can be
(a)
virtual and magnified
(b)
virtual and diminished
(c) virtual
and of same size
(d)
virtual image is not formed
ANS –
virtual and magnified
71. If
the power of a lens is – 2 D, what is its focal length?
(a)
+50 cm
(b)
-100 cm
(c)
-50 cm
(d)
+100 cm
ANS –
-50 cm
72. A
spherical mirror and a spherical lens each have a focal length of -10 cm. The
mirror and the lens are likely to be
(a)
both concave
(b)
both convex
(c)
the mirror is concave and the lens is convex
(d)
the mirror is convex and the lens is concave
ANS –
both concave
73. If
the magnification produced by a lens has a negative value, the image will be
(a)
virtual and inverted
(b)
virtual and erect
(c)
real and erect
(d)
real and inverted
ANS –
real and inverted
74. When
the object is placed between f and 2f of a convex lens, the image formed is
(a)
at F
(b)
at 2F
(c)
beyond 2F
(d)
between O and F
ANS –
beyond 2F
75. Which
mirror can produce a virtual, erect and magnified image of an object?
(a)
Concave mirror
(b)
Convex mirror
(c)
Plane mirror
(d)
Both concave and convex mirrors
ANS –
Concave mirror
76. If
the image is formed in front of the mirror, then the image distance will be
(a)
positive or negative depending on the size of the object
(b)
neither positive nor negative
(c)
positive
(d)
negative
ANS –
negative
77. A
ray of light is travelling from a rarer medium to a denser medium. While
entering the denser medium at the point of incidence, it
(a)
goes straight into the second medium
(b)
bends towards the normal
(c)
bends away from the normal
(d)
does not enter at all
ANS –
bends towards the normal
78. A
student does the experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light passing
through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence. He can get
a correct measure of the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence by
following the labelling indicated in figure:
(a) I
(b)
II
(c)
III
(d)
IV
ANS –
IV
79. An
object is placed 20 cm in front of a plane mirror. The mirror is moved 2 cm
towards the object. The distance between the positions of the original and
final images seen in the mirror is:
(a) 2
cm
(b) 4
cm
(c)
10 cm
(d)
22 cm
ANS- 2
cm
80. A
ray of light that strikes a plane mirror PQ at an angle of incidence of 30o, is
reflected from the plane mirror and then strikes a second plane mirror QR
placed at right angles to the first mirror. The angle of reflection at the
second mirror is:
(a) 300
(b) 450
(c) 600
(d) 900
ANS-
600
81. An
object is placed at 100 mm in front of a concave mirror which produces an
upright image (erect image). The radius of curvature of the mirror is:
(a)
Less than 100 mm
(b)
Between 100 mm and 200 mm
(c)
Exactly 200 mm
(d)
More than 200 mm
ANS-
More than 200 mm
82.
Which position of the object will produce a magnified virtual image, if a
concave mirror of focal length 15 cm is being used?
(a)
10 cm
(b)
20 cm
(c)
30 cm
(d)
35 cm
ANS-
10 cm
83. A
concave mirror produces a magnification of +4. The object is placed:
(a)
At the focus
(b)
Between focus and centre of curvature
(c)
Between focus and pole
(d)
Beyond the centre of curvature
ANS-
Between focus and pole
84. Two
big mirrors A and B are fitted side by side on a wall. A man is standing at
such a distance from the wall that he can see the erect image of his face in
both the mirrors. When the man starts walking towards the mirrors, he finds
that the size of his face in mirror A goes on increasing but that in mirror B
remains the same:
(a)
Mirror A is concave and mirror B is convex
(b)
Mirror A is plane and mirror B is concave
(c)
Mirror A is concave and mirror B is plane
(d)
Mirror A is convex and mirror B is concave
ANS-
Mirror A is concave and mirror B is plane
85. A
ray of light is travelling in a direction perpendicular to the boundary of a
parallel glass slab. The ray of light:
(a)
Is refracted towards the normal
(b)
Is refracted away from the normal
(c) Is
reflected along the same path
(d)
Does not get refracted
ANS-
Does not get refracted
86. A
ray of light passes from a medium X to another medium Y. No refraction of light
occurs if the ray of light hits the boundary of medium Y at an angle of:
(a)
1200
(b)
900
(c)
450
(d) 00
ANS-
900
87. A
lens of focal length 12 cm forms an erect image, three times the size of the
object. The distance between the object and image is:
(a) 8
cm
(b)
16 cm
(c) 24
cm
(d)
36 cm
ANS-
16 cm
88. If
an object is placed 21 cm from a converging lens, the image formed is slightly
smaller than the object. If the object is placed at a distance of 19 cm from
the lens, the image formed is slightly larger than the object. The approximate
focal length of the lens is:
(a)
20 cm
(b)
18 cm
(c)
10 cm
(d) 5
cm
ANS-
10 cm
89. A
student does the experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light passing
through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence. He can get
a correct measure of the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence by
following the labelling indicated in figure:
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS-
D
90.
While performing an experiment on determination of focal length of a convex
lens, four students obtained the image of the same distant tree on the screen
as follows:
Which
diagram shows the formation of image correctly?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS-
D
91. A
student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular slab.
For
measuring the angle of incidence, he must position the protractor in the manner
shown in the figure:
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS-
D
92.
Four students A, B, C and D performed the experiment to determine the focal length
of a concave mirror by obtaining the image of a distant tree on a screen. They
measured the distances between the screen and the mirror as shown in the
diagrams given below:
The
correct way to measure accurate focal length of the mirror is:
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS-
C
93. A
student traces the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular slab
for three different values of angle of incidence (∠i ) namely 300, 450
and 600. He extends the direction of incident ray by a dotted line
and measures the perpendicular distance ‘l’ between the extended incident ray
and the emergent ray.
He will observe
that:
(a)
‘l’ keeps on increasing with increase in angle of incidence
(b)
‘l’ keeps on decreasing with increase in angle of incidence
(c)
‘l’ remains the same for all three angles of incidence
(d)
‘l’ is the maximum for ∠i = 450 and is less than this value for ∠i = 300 and ∠i = 600.
ANS-
‘l’ keeps on increasing with increase in angle of incidence
94.
When a plane mirror is rotated through a certain angle, the reflected ray turns
through twice as much and the size of the image:
(a)
is doubled
(b)
is halved
(c)
becomes infinite
(d)
remains same
ANS-
Remains same
95.
Which statement is true for the reflection of light?
(a)
The angle of incidence and reflection are equal.
(b)
The reflected light is less bright than the incident light.
(c)
The sum of angle of incidence and reflection is always greater than 900
(d)
The beams of incident light after reflection diverge at unequal angles.
ANS-
The angle of incidence and reflection are equal
96. The
image shows the path of incident rays to a concave mirror.
Where
would the reflected rays meet for the image formation to take place?
(a)
behind the mirror
(b)
between F and O
(c)
between C and F
(d)
beyond C
ANS-
Between C and F
97. A
beam of light incident on a mirror forms a real image on reflection. The
reflected beam is:
(a)
parallel
(b)
convergent
(c)
divergent
(d)
not certain
ANS-
Convergent
98. An
object is placed at a distance of 40cm in front of a concave mirror of focal
length 20 cm. The image produced is:
(a)
virtual and inverted
(b)
real and erect
(c)
real, inverted and of the opposite size as that of the object
(d)
real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object
ANS-
real, inverted and of the same size as that of the object
99. A
student conducts an experiment using a convex lens. He places the object at a
distance of 60 cm in front of the lens and observes that the image is formed at
a distance of 30 cm behind the lens. What is the power of the lens?
(a)
0.005 dioptre
(b)
0.05 dioptre
(c) 5
dioptre
(d)
50 dioptre
ANS-
5 dioptre
100.
Image formed by a convex spherical mirror is:
(a)
virtual
(b)
real
(c)
enlarged
(d)
inverted
ANS-
Virtual
101. A
student studies that a convex mirror always forms a virtual image irrespective
of its position. What causes the convex mirror to always form a virtual image?
(a)
because the reflected ray never intersects
(b)
because the reflected ray converges at a single point
(c)
because the incident ray traces its path back along the principal axis
(d)
because the incident ray of a convex mirror gets absorbed in the mirror
ANS-
because the reflected ray never intersects
102. A
10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front pin is formed at 30cm in front
of the mirror. The focal length of this mirror is:
(a)
-30cm
(b)
-20cm
(c)
-40cm
(d)
-60cm
ANS:
-20 cm
103.
Rahul conducts an experiment using an object of height 10 cm and a concave lens
with focal length 20 cm. The object is placed at a distance of 25 cm from the
lens. Can the image be formed on a screen?
(a)
yes, as the image formed will be real
(b)
yes, as the image formed will be erect
(c)
no, as the image formed will be virtual
(d)
no, as the image formed will be inverted
ANS-
No, as the image will be virtual
104. A
student conducts an activity using a concave mirror with focal length of 10 cm.
He placed the object 15 cm from the mirror. Where is the image likely to form?
(a)
at 6 cm behind the mirror
(b)
at 30 cm behind the mirror
(c)
at 6 cm in front of the mirror
(d)
at 30 cm in front of the mirror
ANS-
at 30 cm in front of the mirror
105.
The image of an object placed in front of a convex mirror is formed at
(a)
the object itself
(b)
twice the distance of the object in front of the mirror
(c) half
the distance of the object in front of the mirror
(d)
behind the mirror
ANS-
behind the mirror
106. A
student conducts an activity using a flask of height 15 cm and a concave
mirror. He finds that the image formed is 45 cm in height. What is the magnification
of the image?
(a)
-3 times
(b)
-1/ 3 times
(c)
1/ 3 times
(d) 3
times
ANS-
3 times
107.
Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light from a point source
incident on it?
(a)
concave mirror as well as convex lens
(b)
convex mirror as well as concave lens
(c)
two plane mirrors placed at 90degree to each other
(d)
concave mirror as well as concave lens
ANS-
Concave mirror as well as convex lens
108. A
student studies that the speed of light in air is 300000 km/ sec where that of
speed in a glass slab is about 197000 km/ sec. What causes the difference in
speed of light in these two media?
(a)
difference in optical density
(b)
difference in temperature
(c)
difference in amount of light
(d)
difference in direction of wind flow
ANS-
difference in optical density
109.
Four students showed the following traces of the path of a ray of light passing
through a rectangular glass slab.
The
trace most likely to be correct is that of student:
(a)
I (b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
ANS-
I
110. In an experiment to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab, four students tabulated their observations as given below:
|
Students |
A |
B |
C |
D |
|
∠i |
30° |
30° |
30°, |
30°, |
|
∠r |
18° |
20° |
17° |
21.5° |
|
∠e |
32° |
32.5° |
30° |
34.5° |
Which
student performed the experiment correctly?
(a)
A (b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS-
C
111. A
student does the experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light through a
rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence. He can get a correct
measure of the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence by following the
labelling indicated in figure:
(a)
A (b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS-
D
112. A
student performs the experiment on tracing the path of a ray of light passing
through a rectangular glass slab for different angles of incidence. He measures
the angle of incidence ∠i,
angle of refraction ∠r
and angle of emergence ∠e
for all his observations. He would find that in all cases
(a) ∠i is more than ∠r but (nearly) equal to ∠e
(b) ∠i is less than ∠r but (nearly) equal to ∠e
(c) ∠i is more than ∠e but (nearly) equal to ∠r
(d) ∠i is less than ∠e but (nearly) equal to ∠r
ANS- ∠i is more than ∠r but (nearly) equal to ∠e
113.
The two dots P1 and P2 shown in each of the following diagrams I, II, III and
IV denote the position of two pins in respect of distance and direction for
performing an experiment on tracking the path of a ray of light passing through
a rectangular glass slab. In which one of the four cases, one is likely to get
the best result?
(a)
I (b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
ANS-
III
114. In
an experiment to trace the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular
glass slab, the correct measurement of angles of incidence (i), refraction (r)
and emergence (e) is shown in the diagrams.
(a)
A (b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS-
A
115.
The path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab was traced
and angles measured. Which one out of the following is the correct representation
of an angle of incidence (i), angle of refraction (r) and angle of emergence
(e) as shown in the diagrams:
(a)
I (b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
ANS-
IV
116. An experiment to trace the path of a ray of light through a glass was performed by four students A, B, C and D. They reported the following measurements of angle of incidence i, angle of refraction r and angle of emergence e.
|
Student |
∠i |
∠r |
∠e |
|
A |
30° |
30° |
20° |
|
B |
40° |
50° |
40° |
|
C |
40° |
30° |
48° |
|
D |
40° |
30° |
40° |
Which
student performed the experiment correctly?
(a)
A (b) B
(c) C (d) D
ANS-
D
117.
The correct path of a ray of light passing from air to kerosene oil and from
kerosene oil to water is,
(a)
A (b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS-
D
118. A
ray of light enters air from water and experiences refraction, then
(a) ∠i = ∠r
(b) ∠i < ∠r
(c) ∠i > ∠r
(d) ∠i / ∠r = 0°
ANS- ∠i > ∠r
119.
Four students A, B, C and D traced the paths of incident ray and the emergent
ray by fixing pins P and Q for incident ray and pins R and S for emergent ray
for a ray of light passing through a glass slab.
The
correct emergent ray was traced by the student:
(a)
A (b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS-
B
120. After tracing the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab for four different values of the angle of incidence, a student reported his observations in tabular form as given below:
|
S.No. |
∠i |
∠r |
∠e |
|
I |
30° |
19° |
29° |
|
II |
40° |
28° |
40° |
|
III |
50° |
36° |
50° |
|
IV |
36° |
40° |
59° |
The
best observation is:
(a)
I (b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
ANS-
II
121.
Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a
point source is incident on it?
(a)
Concave mirror as well as convex lens
(b)
Convex mirror as well as concave lens
(c)
Two plane mirrors placed at 90° to each other
(d)
Concave mirror as well as concave lens
ANS-
concave mirror as well as convex mirror
122.
Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image
larger than the actual object?
(a)
When the object is kept at a distance equal to its radius of curvature
(b)
When object is kept at infinity
(c)
When object is placed between the focus and centre of curvature
(d)
When object is kept at a distance greater than its radius of curvature
ANS- When
the object is placed between the focus and centre of curvature
123.
The diagrams showing the correct path of the ray after passing through the
(a)
II and III only
(b) I
and II only
(c)
I, II and III
(d)
I, II and IV
ANS-
I, II and III
124.
You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these
media a ray of light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most?
(a)
Kerosene
(b)
Water
(c)
Mustard oil
(d)
Glycerine
ANS-
Glycerine
125.
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on
a concave mirror as shown in figure?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS-
D
126.
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on
a lens shown in figure?
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
ANS-
A
127. A
child is standing in front of a magic mirror. She finds the image of her head
bigger, the middle portion of her body of the same size and that of the legs
smaller. The following is the order of combinations for the magic mirror from
the top.
(a)
Plane, convex and concave
(b)
Convex, concave and plane
(c)
Concave, plane and convex
(d)
Convex, plane and concave
ANS-
Concave, plane and convex
128.
Light travel fastest in
(a)
Water
(b)
Air
(c)
Glass
(d)
Diamond
ANS-
Air
129. A
student used a device (X) to obtain/focus the image of a well illuminated
distant building on a screen (S) as shown alongside in the diagram. Select the
correct statement about the device (X).
(a)
This device is a concave lens of focal length 8 cm.
(b)
This device is a convex mirror of focal length 8 cm.
(c)
This device is a convex lens of focal length 4 cm.
(d)
This device is a convex lens of focal length 8 cm.
ANS- This
device is a convex lens of focal length 8 cm.
130. A
student obtains a sharp image of the distant window (W) of the school
laboratory on the screen (S) using the given concave mirror (M) to determine
its focal length. Which of the following distances should he measure to get the
focal length of the mirror?
(a)
MW
(b)
MS
(c)
SW
(d)
MW- WS
ANS-
MS
131.
The mirror having reflection surface curved outwards is the-
(a)
plane mirror
(b)
concave mirror
(c)
convex mirror
(d)
cylindrical mirror
ANS-
Convex mirror
132.
The mirror having reflecting surface curved inwards is the-
(a)
plane mirror
(b)
convex mirror
(c)
cylindrical mirror
(d)
concave mirror
ANS-
Concave mirror
133.
The deviation of light ray from its path when it travels from one transparent
medium to another transparent medium is called
(a) reflection
(b)
refraction
(c)
dispersion
(d)
scattering
ANS-
refraction
134.
Convex lens is also known as,
(a)
converging lens
(b)
diverging lens
(c)
radial lens
(d)
axial lens
ANS-
Converging lens
135.
The image which is formed behind the mirror is,
(a)
real image
(b)
virtual image
(c)
blue image
(d)
partial image
ANS-
virtual image
























Nice
ReplyDelete